Northern millennials less likely to live into their 50s than their southern English counterparts
By Professor

There is a stark disparity in wealth and health between people in the north and south of England, commonly referred to as England’s “north-south divide”. The causes of this inequality are complex; it’s influenced by the environment, jobs, migration and lifestyle factors – as well as the long-term political power imbalances, which have in the south, especially in and around London.
Life expectancy is also lower in the north, mainly because the region is more deprived. But of national mortality data highlights a shockingly large mortality gap between young adults, aged 25 to 44, living in the north and south of England. This gap first emerged in the late 1990s, and seems to have been growing ever since.
In 1995, there were 2% more deaths among northerners aged 25 to 34 than southerners (in other words, 2% “excess mortality”). But by 2015, northerners in this age group were 29% more likely to die than their southern counterparts. Likewise, in the 35 to 44 age group, there was 3% difference in mortality between northerners and southerners in 1995. But by 2015, there were 49% more deaths among northerners than southerners in this age group.
Excess mortality in the north compared with south of England by age groups, from 1965 to 2015. Follow the lines to see that people born around 1980 are the ones most affected around 2015.
While mortality increased among northerners aged 25 to 34, and plateaued among 35 to 44-year-olds, southern mortality mainly declined across both age groups. Overall, between 2014 and 2016, northerners aged 25 to 44 were 41% more likely to die than southerners in the same age group. In real terms, this means that between 2014 and 2016, 1,881 more women and 3,530 more men aged between 25 and 44 years died in the north, than in the south.
What’s killing northerners?
To understand what’s driving this mortality gap among young adults, our team of researchers looked at the causes of death from 2014 to 2016, and sorted them into eight groups: accidents, alcohol related, cardiovascular related (heart conditions, diabetes, obesity and so on), suicide, drug related, breast cancer, other cancers and other causes.
Controlling for the age and sex of the population in the north and the south, we found that it was mostly the deaths of northern men contributing to the difference in mortality – and these deaths were by cardiovascular conditions, alcohol and drug misuse. Accidents (for men) and cancer (for women) also played important roles.
From 2014 to 2016, northerners were 47% more likely to die for cardiovascular reasons, 109% for alcohol misuse and 60% for drug misuse, across both men and women aged 25 to 44 years old. Although the national rate of death from cardiovascular reasons , the longstanding gap between north and south remains.
Death and deprivation
The gap in life expectancy between north and south is usually put down to socioeconomic deprivation. We considered further data for 2016, to find out if this held true for deaths among young people. We found that, while two thirds of the gap were explained by the fact that people lived in deprived areas, the remaining one third could be caused by some unmeasured form of deprivation, or by differences in culture, infrastructure, migration or extreme weather.
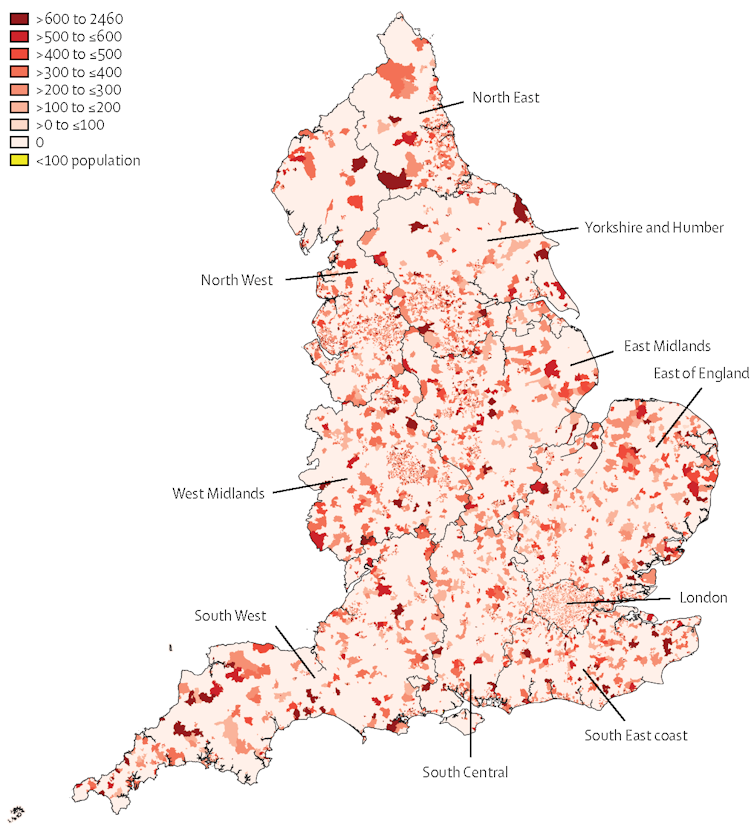
Mortality for people aged 25 to 44 years in 2016, at small area geographical level for the whole of England.
Northern men faced a higher risk of dying young than northern women – partly because overall mortality rates are higher for men than for women, pretty much at every age, but also because men tend to be . Although anachronistic, the expectation to have a job and be able to sustain a family weighs more on men. Accidents, alcohol misuse, drug misuse and suicide are all strongly associated with low socioeconomic status.
Suicide risk is twice as high among the most deprived men, compared to the most affluent. Suicide risk with unemployment, and substantial increases in suicide have been observed during periods of recession – especially among men. tells us that unskilled men between ages 25 and 39 are between ten and 20 times more likely to die from alcohol-related causes, compared to professionals.
Alcohol underpins the steep increase in liver cirrhosis deaths in Britain from the 1990s – which is when the north-south divide in mortality between people aged 25 to 44 also started to emerge. has shown that men in this age group, who live in the most deprived areas, are five times more likely to die from alcohol-related diseases than those in the most affluent areas. For women in deprived areas, the risk is four times greater.
It’s also widely known that mortality rates for cancer , and people have worse survival rates in places where smoking and alcohol abuse is more prevalent. Heroin and crack cocaine addiction and deaths from drug overdoses are also with deprivation.
The greater number of deaths from accidents in the north should be considered in the context of transport infrastructure investment, which is heavily skewed towards the south – especially London, which enjoys the lowest mortality in the country. What’s more, if reliable and affordable public transport is not available, people will drive more and expose themselves to higher risk of an accident.
Deaths for young adults in the north of England have been increasing compared to those in the south since the late 1990s, creating new health divides between England’s regions. It seems that persistent social, economic and health inequalities are responsible for a growing trend of psychological distress, despair and risk taking among young northerners. Without major changes, the extreme concentration of power, wealth and opportunity in the south will continue to damage people’s health, and worsen thenorth-south divide.![]()
, Professor in Data Science and Health Services Research,
This article is republished from under a Creative Commons license. Read the .